- Published on
IntelliJ는 왜 Arrays.asList대신 Collections.singletonList를 추천해줄까?
- Authors
- Name
- 윤종원
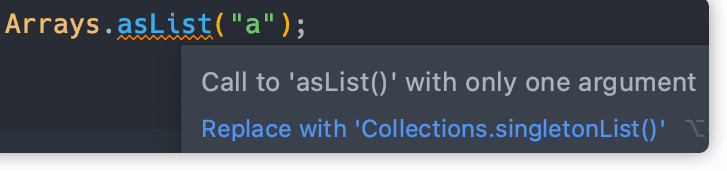
Intellij를 사용하다 보면 Arrays.asList 함수를 이용해서 리스트를 전달해 줄 때가 많다. 이 때 전달하는 원소의 개수가 1개인 경우 Intellij는 위와 같이 Arrays.asList 대신 Collections.singletonList를 사번 찾아보았다.
Arrays.asList
우선 Arrays.asList의 구현은 아래와 같다.
public class Arrays {
// ...
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) {
return new ArrayList<>(a);
}
private static class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2764017481108945198L;
private final E[] a;
ArrayList(E[] array) {
a = Objects.requireNonNull(array);
}
// ...
}
}
Arrays의 내부 클래스인 ArrayList를 생성해서 반환하는 것을 알 수 있다. 또한 이 List는 크기가 고정되어 있어 add나 remove 등을 호출하면 UnsupportedOperationException을 던진다.
실제로 Arrays 클래스는 AbstractList 추상 클래스를 상속받고 있으며 add나 remove 등 List의 크기를 변경하는 메소드를 오버라이드하지 않는다. 또한 이러한 메소드는 AbstractList에 UnsupportedOperationException를 던지도록 구현되어 있다.
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E> {
// ...
public void add(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public E remove(int index) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
// ...
}
즉, Arrays.asList는 Arrays 내부에 구현된 ArrayList를 생성해서 던지며 이는 크기가 고정된 List다. 내부적으로도 단순히 배열을 저장하고, get과 set 메소드 등을 지원해주는 정도이다.
Collections.singletonList
Collections.singletonList의 구현은 아래와 같다.
public class Collections {
// ...
public static <T> List<T> singletonList(T o) {
return new SingletonList<>(o);
}
private static class SingletonList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3093736618740652951L;
private final E element;
SingletonList(E obj) {element = obj;}
}
// ...
}
Collections의 내부 클래스인 SingletonList를 생성해서 반환하는 것을 알 수 있다. 또한 ArrayList와 다르게 요소 하나를 저장하는 것을 알 수 있다. ArrayList는 객체의 배열을 저장한다.
실제로 Intellij는 Arrays.asList보다 Collections.singletonList가 메모리를 효율적으로 사용하므로 Collections.singletonList를 사용할 것을 권장하고 있다. 객체 배열 대신 단일 객체만을 저장하니 메모리 사용이 적을 것이라 예상할 수 있다.
또한 SingletonList는 ArrayList와는 다르게 불변이다. 따라서 add나 remove는 물론 set 등의 메소드 또한 사용하지 못한다. 만약 이를 호출하면 UnsupportedOperationException를 던진다.
즉, ArrayList는 List의 크기가 고정되어 있을 뿐 수정은 가능하다. 하지만 SingletonList는 불변으로 크기가 1로 고정되어있으며 수정 또한 불가능하다. 또한 후자를 사용해서 메모리를 아낄 수 있다.
Arrays.asList와 Collections.singletonList의 메모리 차이
실제로 메모리가 얼마나 차이가 나는지 궁금해서 아래 코드를 사용해서 테스트해보았다.
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("Arrays.asList : " + getBytesFromList(Arrays.asList("b")));
System.out.println("Collections.singletonList : " + getBytesFromList(Collections.singletonList("b")));
}
public static long getBytesFromList(List list) throws IOException {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
out.writeObject(list);
out.close();
return baos.toByteArray().length;
}
각 List의 메모리 사용량 계산은 여기서 얻을 수 있었다.
Arrays.asList : 117
Collections.singletonList : 91
결과는 위와 같았다. 실제로 Collections.singletonList가 Arrays.asList의 77% 정도의 메모리를 사용하는 것을 알 수 있다.
결론
Arrays.asList와 Collections.singletonList가 뭐가 다른지 알아보기 위해서 실제 구현을 살펴보았고 메모리 사용량때문에 후자를 권장한다는 것 또한 알 수 있었다. 또한 메모리를 적게 쓴다면 얼마나 적게 쓰는지 또한 실험을 통해 알아보았다.
singletonList의의 경우 내부적으로 요소 하나만을 저장하는데 다른 메소드 호출 성능 또한 뛰어날 지가 궁금해졌다.